Understanding the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to Fibroadenoma Vs Cancer Ultrasound
If you’ve ever had a lump in your breast, the first thought that probably crossed your mind was “cancer”. It’s a scary word and understandably so. However, not all lumps are cancerous. In fact, one of the most common types of benign breast lumps is fibroadenoma. But how can you tell the difference between fibroadenoma and cancer? That’s where ultrasound comes in. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about fibroadenoma vs cancer ultrasound and how it can help diagnose these two conditions accurately. So grab a cup of coffee and let’s get started!
What is Fibroadenoma?
A fibroadenoma is a harmless, non-cancerous tumor that commonly affects young women between the ages of 15 and 35. Fibroadenomas are usually small, ranging in size from a pea to a walnut, and feel firm and rubbery to the touch. While they can occur in both breasts, they are more commonly found in just one.
Fibroadenomas typically don’t cause any pain or other symptoms. However, some women may experience tenderness or pain in their breast when the tumor grows large enough to press against surrounding breast tissue.
The exact cause of fibroadenomas is unknown. However, they tend to run in families and may be associated with certain genetic mutations. Additionally, certain hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause may also contribute to their development.
While most fibroadenomas don’t require treatment, some women may choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons or if they are causing pain or uncomfortable symptoms. Surgery is the only way to remove a fibroadenoma and can be done using either local anesthesia (numbing medication) or general anesthesia (putting you to sleep).
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a disease caused by the abnormal growth of cells. There are many different types of cancer, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment options. Fibroadenoma is a type of cancer that affects the breast tissue. It is most common in young women and typically does not require treatment. However, if the tumor grows larger than 3 cm, it may need to be removed surgically.
Differences Between Fibroadenoma and Cancer
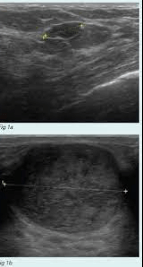
There are several key differences between fibroadenoma and cancer that can be observed via ultrasound. These include:
-Fibroadenomas tend to be well-circumscribed, while cancers are often more diffuse or poorly defined.
-Fibroadenomas typically have a smooth margin, while cancers may have irregular or spiculated margins.
-Fibroadenomas are usually homogeneous in echogenicity, while cancers may be heterogeneous.
-Doppler studies of fibroadenomas typically show no vascularity, while cancers may show increased vascularity.
Early Detection of Breast Cancer
According to the National Cancer Institute, early detection of breast cancer is one of the most important things you can do for your health. There are two main types of breast cancer: ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma starts in the milk ducts and is the most common type of breast cancer. Lobular carcinoma starts in the lobules, which are the glands that produce milk.
If you feel a lump in your breast, it does not necessarily mean you have cancer. In fact, most lumps are benign (noncancerous). However, if you have a family history of breast cancer or are at high risk for the disease, it is important to talk to your doctor about any lumps so they can be properly evaluated.
There are two main types of mammograms: screening mammograms and diagnostic mammograms. Screening mammograms are used to check for breast cancer in women who have no symptoms. Diagnostic mammograms are used to check for breast cancer in women who have symptoms or who have had an abnormal screening mammogram.
If you have a family history of breast cancer or are at high risk for the disease, you may need to start getting mammograms at an earlier age than 50 years old. You may also need to get them more often than every two years. Your doctor can tell you how often you should get a mammogram based on your individual risk factors.
When to See a Doctor
If you have any concerns about a lump in your breast, it’s important to see a doctor right away. Early detection is key to successful treatment of breast cancer.
Your doctor will likely order a mammogram and/or an ultrasound to help determine if the lump is cancerous or benign. There are some key differences between the two types of lumps, which can help your doctor make a diagnosis.
Fibroadenomas are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that commonly occur in women under the age of 30. They are firm, round lumps that are usually moveable and not attached to surrounding tissue. Fibroadenomas typically don’t cause any symptoms and don’t require treatment.
Breast cancer, on the other hand, is much more serious. Breast cancer can occur at any age and affects both men and women. Breast cancer lumps are usually hard, irregularly shaped, and may be attached to surrounding tissue. They also often cause symptoms like nipple discharge or changes in the appearance of the nipple.
If you have any concerns about a lump in your breast, it’s important to see a doctor right away for further testing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is essential to remember that fibroadenoma vs cancer ultrasound can be tricky to differentiate between. However, with a thorough and comprehensive understanding of the differences between them, you will be able to make an informed decision about whether or not further tests are necessary. If in doubt, always contact your doctor for advice on how best to proceed.




