Decoding Breast Cancer Ultrasound Images: A Comprehensive Guide
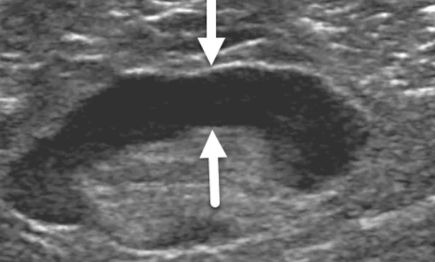
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death among women, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Ultrasound imaging has become a valuable tool in breast cancer screening as it can detect abnormalities that may not be visible on mammograms. However, interpreting ultrasound images can be challenging even for medical professionals. In this comprehensive guide, we will decode breast cancer ultrasound images and provide you with a better understanding of what to look out for during screenings. So let’s get started!
Ultrasound Basics
Ultrasound is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures. The process involves placing a transducer, which emits and receives sound waves, on the skin surface over the area being examined.
The sound waves produced by the transducer penetrate through the skin and bounce off internal organs or tissues, creating echoes that are recorded and displayed as real-time images on a screen. Ultrasound imaging is commonly used for examining soft tissue structures such as breasts, liver, kidneys, uterus, and ovaries.
Unlike other imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans that use ionizing radiation to produce images, ultrasound does not expose patients to harmful radiation. Ultrasound can also be used in real-time during surgery or other procedures to guide needles or catheters into specific areas of the body accurately.
Ultrasound is an incredibly useful tool in modern medicine due to its safety profile and versatility in various diagnostic applications.
Breast Imaging
Breast imaging is a diagnostic tool used to examine the structure of breast tissue. The purpose of breast imaging is to detect any abnormalities or changes in breast tissue that may be indicative of cancer or other conditions.
There are several types of breast imaging, including mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Mammography is the most common type of screening for breast cancer and involves taking X-ray images of the breasts. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, while MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images.
Breast imaging plays an important role in detecting early stage breast cancer when it’s easier to treat. Women who have a family history or other risk factors for developing breast cancer should undergo regular screenings as recommended by their healthcare provider.
While mammography remains the gold standard for screening, ultrasound has become an increasingly popular method due to its ability to detect small lesions that may not be visible on mammograms alone. Additionally, ultrasound does not expose patients to radiation like mammography does.
Early detection through regular screenings with various forms of breast imaging can lead to better outcomes for women diagnosed with breast cancer.
Breast Ultrasound Interpretation
Breast ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses sound waves to create images of breast tissue. These images are interpreted by trained radiologists or sonographers, who can identify any abnormalities or lesions present in the breast.
Interpretation of breast ultrasound images involves analyzing the size, shape, and texture of any detected masses or lesions. The characteristics of these abnormalities are used to determine whether they are benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
One important aspect of interpretation is identifying the location and depth of any abnormality within the breast tissue. This information helps physicians plan for further testing and treatment if necessary.
The interpretation process also involves assessing blood flow patterns within the breast tissue using Doppler ultrasound technology. A lack of blood flow to an area may indicate that it is cancerous.
Interpreting breast ultrasound images requires extensive training and experience in order to accurately identify potential cancerous lesions while minimizing false positives.
Breast Cancer Screening Methods
Breast cancer screening is an important aspect of breast health and early detection. There are different methods used for breast cancer screening, including mammography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and clinical breast exams.
Mammography is the most widely used method for breast cancer screening. It involves taking X-ray images of the breasts to look for any abnormalities or changes that may indicate the presence of cancer cells.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of the inside of the breasts. This method can be particularly useful in detecting lumps or masses that may not be visible on a mammogram.
MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the breast tissue. It can be especially helpful in identifying small tumors that may not show up on other types of scans.
Clinical breast exams involve a healthcare provider physically examining a woman’s breasts and underarms for any signs of lumps or other abnormalities.
It’s important to note that no single method is foolproof when it comes to detecting breast cancer. A combination of screenings, along with regular self-exams and awareness about your own body, can help increase your chances of catching potential issues early on.
The Different Types of Breasts
Breasts come in different shapes and sizes, which can affect the accuracy of breast cancer screening methods like ultrasound. The two main types of breasts are fatty and dense. Fatty breasts have more fat tissue than glandular or fibrous tissue, making them easier to examine on an ultrasound image.
Dense breasts have less fat tissue and more glandular or fibrous tissue, which makes it harder for ultrasounds to detect cancerous lesions. Women with dense breasts may need additional imaging tests like mammograms or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to screen for breast cancer accurately.
Breast shape also affects how easily a lesion can be seen on an ultrasound image. Round-shaped breasts make it easier to detect small abnormalities whereas elongated or tubular shaped breasts present unique challenges as they require specific techniques during the scanning process.
It’s important for healthcare providers performing ultrasounds to consider these factors when interpreting breast images accurately. By understanding the differences between different types of breasts, we can improve our ability to detect potential cancers early through regular screenings and potentially save lives.
Ultrasound-Detectable Cancerous Lesions
Breast ultrasound is an effective screening method for detecting cancerous lesions early. The earlier the detection, the better chances of successful treatment and survival. There are several types of ultrasound-detectable breast cancer lesions.
Solid masses are common types of cancerous lesions that appear as firm lumps in the breast tissue. They can be seen on an ultrasound scan as solid areas with irregular shapes and rough edges.
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can mimic a tumor but they aren’t usually considered to be dangerous or life-threatening. However, if there’s any suspicion about a cystic lesion, it should undergo further testing to confirm its nature.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is another form of breast cancer detectable through ultrasound scans. It arises within ducts leading from milk glands inside the breast and often presents itself as calcifications or specks visible on mammograms.
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is yet another type of invasive breast cancer detected by ultrasounds. IDC starts in milk ducts but spreads beyond them into other parts of the body such as lymph nodes or organs like liver or lungs.
Therefore, regular self-examinations coupled with routine screening using ultrasonography ensures early detection and prompt treatment if necessary when abnormal growth appears in your breasts during imaging tests; these exams could help detect Ultrasound-Detectable Cancerous Lesions before they become problematic later on down the line!
Conclusion
In the fight against breast cancer, early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial. Breast ultrasound imaging plays a significant role in identifying potential abnormalities, especially when used in conjunction with other screening methods such as mammography. By understanding the basics of ultrasound technology and how to interpret breast cancer ultrasound images, healthcare professionals can better serve their patients during this critical time.
The different types of breasts should also be taken into consideration while interpreting these images to ensure accuracy. With the advancements in medical technology, we now have a greater understanding of various ultrasound-detectable cancerous lesions that may help save countless lives through timely intervention.
Ultimately, having comprehensive knowledge about breast ultrasounds and their interpretation is vital for both physicians and patients alike. This guide serves as an excellent starting point for those looking to delve deeper into this essential aspect of breast health care. Remember that regular screenings remain key to maintaining good overall health – so don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider if you have concerns or questions about your own well-being!




