Canker sore vs cancer of the mouth: What’s The Difference?
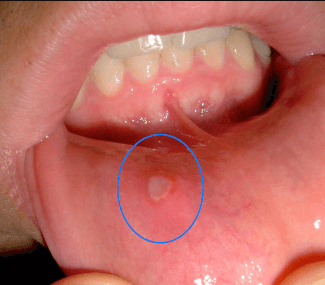
Canker sores and cancer of the mouth are two terms that often get confused. This blog post will explore canker sore vs cancer of the mouth and their symptoms. We will also discuss the treatments available for each one, so that you can make an informed decision about which condition is right for you.
What are Canker Sores?
Canker sores are skin irritants that most commonly affect the mouth. They’re also known as oral lichen planus (OLP) and can be accompanied by pain, redness, and swelling. Canker sores are caused by an overgrowth of the bacteria Candida albicans. This yeast forms colonies on the skin’s surface, which can cause inflammation and tissue damage. Although canker sores can be a sign of mouth cancer, there is no clear-cut connection between the two conditions. It’s important to get evaluated by a doctor if you experience any following symptoms:
ulcers that do not heal within two weeks, swelling or tenderness around the ulcer, a fever, loss of appetite In general, canker sores can be treated with topical medications such as anti-fungal ointments or antibiotics. If your condition worsens or doesn’t improve after taking these treatments, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the sore.
Types of Canker Sores
There are different types of canker sores, each with its distinguishing features. The most common type is the oral herpes virus (OHV) canker sore, which causes painful blisters that often appear on the lip or around the mouth. OHSV-1 is the type most commonly associated with cold sores, while OHSV-2 is more common in people who contract herpes from other sources, such as kissing or sexual contact. Other types of canker sores include shingles (herpes zoster), chickenpox (varicella zoster), and human papillomavirus (HPV) related sores.
The distinction between these types of canker sores often hinges on the cause of infection. Oral herpes lesions are typically caused by OHV, although they can also be caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2 if someone is infected with either virus before developing a lesion. Shingles lesions are caused by varicella zoster virus and are generally much less painful than oral herpes lesions. Chickenpox lesions are caused by variola virus and usually look like small bumps on the skin that may blister and turn red or purple when irritated. HPV related lesions may be caused by any one of several HPV viruses, but are typically more severe and may lead to cancer if left untreated.
Symptoms of Canker Sores
There is a big difference between canker sores and cancer of the mouth, but a virus causes both. Canker sores are small, painful ulcers that form inside the cheeks or lips. They generally go away within a few weeks without treatment. Cancer of mouth is more serious condition that may lead to death if not treated. It most often affects people in their 60s or older and occurs when cells in the mouth grow uncontrolled (known as malignant transformation). Most common symptoms are pain, swelling, and redness around the lips or tongue.
How to Treat Canker Sores
Canker sores, also known as oral herpes, are small, painful ulcers that form on the lip or tongue. They can be caused by the HSV-1 virus (the most common cause) or the HSV-2 virus (more common in people with multiple sexual partners). Canker sores heal within few weeks but occasionally require antibiotic treatment. They’re not cancer and don’t usually spread to other body parts. However, if you have canker sores and they become infected with cancerous cells, your health may be in danger. Cancer of mouth is a more serious condition that can occur when HSV-1 or HSV-2 infections reach the lower jawbone or throat. It can lead to impaired speech and swallowing, and death may occur if not treated. If you experience any changes in your mouth, including pain, swelling, redness, or a change in your tooth appearance (due to tumor), please see your doctor immediately.
Cancer of the Mouth: What’s The Difference?
Cancer of the mouth (malignant lip cancer) is a serious medical condition. It’s caused by abnormal cells that grow in the mouth’s tissues. The most common type of mouth cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, the most common form of skin cancer. Other types of cancer can also occur in the mouth, but they’re rare.
Cancer of the mouth can be dangerous and difficult to treat. If caught early, it can be cured with surgery or radiation therapy. If left untreated, however, it can spread to other body parts (metastasize). Cancer of the mouth is responsible for about 1 in 5 oral cancers and is one of the most common types of cancer in women.
There are some key differences between cancer of the mouth and cancer of the skin. For example, cancer of the mouth usually occurs on white tissue (the lining of your throat), while skin cancers occur on all types and colors of skin. Cancerous cells in cancer of the mouth tend to grow faster than cells in skin cancers. And because cancerous cells in cancerous mouths spread more easily to other parts of your body, treatment for this disease tends to be more aggressive than treatment for skin cancers.
Treatment Options for Cancer of the Mouth
Cancer of the mouth is a highly treatable cancer. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of the cancer. The most common treatment for cancer of the mouth is surgery. Other common treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal therapy. Most people with cancer of the mouth can expect to survive for at least five years after treatment is completed.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing a sore that doesn’t seem to go away, or if you have any concerns at all about your mouth, it’s important to see a doctor. Canker sores are often confused with cancer of the mouth, but there is a big difference between the two. Cancer of the mouth is much more serious and can require surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and/or oral implants to treat. Canker sores are caused by an infection in the salivary glands and typically heal on their own within 2-6 weeks without any treatment other than pain relief medication. If you think you may have a canker sore vs cancer of the mouth, it’s important to get checked out by your doctor as soon as possible.




