Can Ultrasound Detect Cancer? A Look into the Science Behind the Diagnostic Method
Have you ever wondered if ultrasound can detect cancer? With the advancement of technology, diagnostic methods have also evolved to become more accurate and efficient. One such method is the use of ultrasound in detecting cancer. Ultrasound has been proven effective in diagnosing various medical conditions but can it be relied upon for cancer detection? In this blog post, we will take a closer look at how ultrasound works and its effectiveness as a tool for detecting cancer. So grab a cup of coffee and get ready to delve into the science behind this diagnostic method!
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal organs and tissues. It is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve the use of radiation, making it a safe option for patients.
During an ultrasound exam, a sonographer applies gel to the skin over the area being examined before moving a transducer back and forth over the skin. The transducer emits sound waves which bounce off internal structures within the body, creating echoes that are picked up by sensors in the transducer.
These echoes are then converted into images by computer software, allowing doctors to visualize various structures inside the body such as organs, blood vessels or tissue masses. Ultrasound can also be used to measure blood flow through vessels and detect abnormalities in fetal development during pregnancy.
Ultrasound has become an essential tool for medical diagnosis due to its ability to provide real-time visualization of internal structures without exposing patients to harmful ionizing radiation. Additionally, it is relatively inexpensive compared with other imaging modalities making it more accessible for patients who require frequent monitoring or follow-up examinations.
How Does Ultrasound Work?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal organs and tissues in the body. Unlike other imaging methods, such as X-rays and CT scans, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation.
When an ultrasound examination is performed, a small handheld device called a transducer is placed on the skin over the area being examined. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that penetrate through the skin and bounce off internal structures, creating echoes.
These echoes are then detected by the transducer and converted into electrical signals, which are processed by a computer to create detailed images of the internal structures in real time.
The amount of reflection or echo received depends on how dense or solid an object is. For example, bone reflects almost all of the sound wave energy back to the transducer, while fluid-filled structures like cysts allow most of it to pass through.
By analyzing these reflections or echoes from different angles using advanced software algorithms, doctors can visualize and assess various organs, blood vessels, and tissues within seconds with great accuracy.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure that allows medical professionals to diagnose many conditions quickly without exposing patients’ bodies to harmful radiation levels.
What Are the Different Types of Ultrasounds?
Ultrasound is a highly versatile diagnostic tool that can be used to visualize various parts of the body. There are different types of ultrasounds, each with their own unique features and purposes.
The most common type of ultrasound is the standard 2D ultrasound. This type uses high-frequency sound waves to produce two-dimensional images of organs and tissues in real-time. It’s commonly used during pregnancy to monitor fetal development, but it can also be used for other diagnostic purposes.
Another type of ultrasound is the 3D ultrasound, which creates three-dimensional images by taking multiple 2D scans from different angles. This type provides more detailed images and can be useful for detecting abnormalities or structural issues in fetuses or other organs.
A newer technology called the 4D ultrasound combines real-time imaging with 3D views, allowing doctors to see movement in addition to structure. This has proven particularly helpful in obstetrics as parents get a glimpse into what their baby looks like before birth.
There’s the Doppler ultrasound which utilizes sound waves that bounce off moving blood cells within vessels providing information on blood flow speeds and directionality — making it great for assessing risks associated with cardiovascular diseases.
These different types allow medical professionals greater flexibility when diagnosing patients using ultrasounds depending on specific needs rather than being limited by one-size-fits-all approach
How Is Ultrasound Used to Diagnose Cancer?
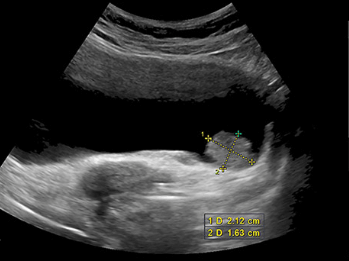
Can ultrasound detect cancer? When it comes to cancer diagnosis, ultrasound is one of the many diagnostic methods used by doctors. Ultrasound works by using high-frequency sound waves that bounce off internal organs and tissues, creating echoes that are then used to create a visual image of the area being examined.
One way ultrasound is used in cancer diagnosis is through breast examinations. During a breast ultrasound, a technician uses an instrument called a transducer to send sound waves into the breast tissue. The echoes produced from these sound waves can help detect any abnormalities or changes within the tissue.
In addition to breast examinations, ultrasounds can also be used for diagnosing other types of cancers such as liver, thyroid, and ovarian cancer. For example, when examining the liver with an ultrasound machine, doctors look for any irregularities or masses on the organ’s surface.
While ultrasounds are helpful in detecting cancerous growths at early stages compared to other imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans; however they might not be able to determine whether those growths are benign or malignant without further testing.
While there may be limitations to using ultrasound as a diagnostic tool for certain cancers; healthcare professionals continue utilizing this method due to its non-invasive nature and ability to identify potential issues before symptoms develop.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Ultrasound to Detect Cancer?
Ultrasound is a widely used diagnostic tool for detecting cancer in patients. One of the main advantages of using ultrasound to detect cancer is that it is non-invasive and does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation, making it relatively safe compared to other imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans.
Another benefit of ultrasound is its ability to visualize soft tissues with high accuracy, allowing doctors to identify tumors at an early stage when they are small and easier to treat. Ultrasound can also be used for guidance during biopsy procedures, helping doctors accurately locate the tumor site and collect tissue samples without causing unnecessary trauma.
However, there are some limitations associated with using ultrasound for cancer diagnosis. For instance, ultrasound may not be able to detect certain types of cancers that do not produce distinct masses or lumps on imaging tests. Additionally, the quality of images obtained by ultrasound may vary depending on factors such as body habitus and operator skill level.
While ultrasounds generally have no known harmful effects on the body; however like any medical procedure there is always a slight risk involved particularly if contrast agents are used which could cause allergic reactions or discomfort in rare cases.
Though despite these limitations, ultrasonography remains one of the most commonly utilized methods for diagnosing various forms of cancer due its many benefits outweighing drawbacks in most cases.
Conclusion
Ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool that has proven to be an effective method for detecting cancer in many cases. It is non-invasive, painless, and provides real-time images, making it an ideal technique for monitoring the progression of cancer treatment.
However, while ultrasound can detect certain types of cancers with high accuracy rates, there are limitations to its effectiveness. It may not be able to detect early-stage tumors or identify certain types of cancers.
Ultimately, the decision on whether or not to use ultrasound as a diagnostic method for cancer detection depends on several factors such as the type and stage of cancer being screened for. Consult with your doctor if you have any concerns about using ultrasound as a diagnostic tool.
In combination with other methods such as biopsies and blood tests, ultrasound can play an important role in the detection and management of various types of cancers.




